An automatic transfer switch (ATS) detects power outages and switches your load from utility to generator instantly, ensuring continuous power. There are different types, such as open or closed changeover, manual or automatic, and single-source or multiple-source switches, each suited to specific needs. Choosing the right one depends on your system requirements, safety, and budget. Keep exploring, and you’ll discover how to pick and maintain the perfect ATS for your setup.
Key Takeaways
- Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS) detect power loss and switch seamlessly between utility and backup generator to ensure continuous power.
- Choose between open and closed transition ATS based on your need for power interruption or seamless transfer.
- Single-source ATS are simple and ideal for one generator, while multiple-source switches manage multiple power inputs.
- Manual ATS require physical operation, whereas automatic ATS respond instantly to power outages for critical systems.
- Proper installation, regular maintenance, and safety protocols are essential for system reliability and safety.
What Is an Automatic Transfer Switch?

Have you ever wondered how backup power systems automatically switch between utility and generator power? An automatic transfer switch (ATS) makes this possible. When a power outage occurs, the ATS detects the loss of utility power and immediately switches to your backup generator. This process is seamless, ensuring your appliances and critical systems stay operational without manual intervention. Once utility power is restored, the ATS switches back to the grid and turns off the generator. This automatic action minimizes downtime and prevents damage caused by power interruptions. Essentially, an ATS provides peace of mind by ensuring continuous power supply during outages, making it a crucial component of reliable backup power systems. It’s a smart device that keeps your home or business running smoothly when the lights go out. Reliable operation is essential for maintaining a steady power supply in critical situations.
The Main Types of Transfer Switches

Understanding the main types of transfer switches helps you choose the right system for your needs. You’ll find differences between automatic and manual switches, as well as open and closed designs. Let’s explore how these options impact reliability and safety. Ethical Hacking techniques can also be used to evaluate the security of your electrical systems, ensuring they are protected against potential cybersecurity threats.
Automatic vs. Manual
Are automatic and manual transfer switches truly different in how they protect your power supply? Yes, they operate differently. Manual transfer switches rely on manual operation—meaning you have to physically switch the power source yourself during an outage. They give you control but require your intervention. Automatic transfer switches, on the other hand, feature automatic detection of power loss. They sense when the main power fails and switch seamlessly to backup power without needing your input. This quick response minimizes downtime and keeps your systems running smoothly. The key difference is that automatic switches provide hands-free operation, while manual switches depend on you to act. Both serve important roles, but your choice depends on how much control and convenience you desire. Additionally, reliability is a critical factor to consider, as automatic switches often incorporate advanced sensing technology to ensure consistent performance.
Open vs. Closed
Open and closed transfer switches represent the two main designs you’ll encounter, each serving different needs. Open switches disconnect the load from the utility first, then connect to backup power, offering high switch reliability but momentary power loss. Closed switches, or overlap switches, connect both sources briefly, ensuring seamless power transfer but potentially risking back-feeding issues. Understanding trailer music techniques can help you appreciate how sound design can complement these switching methods by creating a smooth audio transition during power shifts.
- Open switches prioritize switch reliability and are ideal for critical backup power needs.
- Closed switches reduce power interruption during transfer, suitable for sensitive equipment.
- Open switches are simpler and generally more affordable.
- Closed switches require careful installation to avoid back-feeding hazards.
Choosing between them depends on your backup power requirements and the importance of continuous, reliable power during transfers.
Single-Source vs. Multiple-Source Switches

Have you ever wondered how an automatic transfer switch chooses between different power sources? Single-source switches connect your load to only one power source at a time, making them simple and cost-effective. They’re ideal if you rely on a single generator, ensuring compatibility and straightforward operation. Multiple-source switches, on the other hand, can manage two or more power sources simultaneously, offering greater flexibility. They automatically select the best available source, which is useful for complex setups or multiple generators. When choosing between them, consider your generator compatibility and switch enclosure options. Single-source switches are often more compact and easier to install, while multiple-source models may require larger enclosures. Your choice depends on your power needs and system complexity.
Open Transition vs. Closed Transition Switches
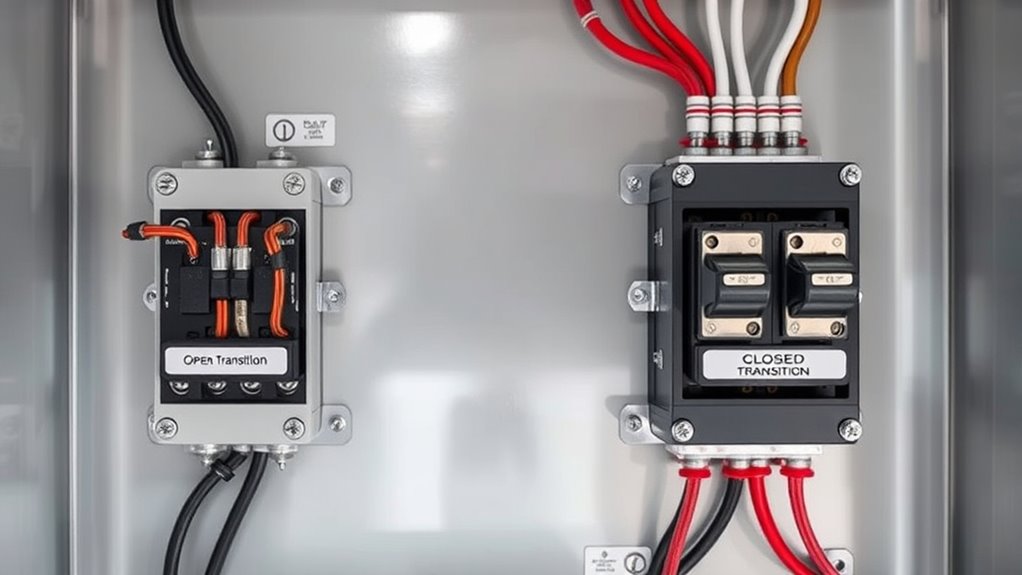
Choosing between open progression and closed *changeover* automatic transfer switches depends on how smoothly you want your power transfer to occur. Open *changeover* switches disconnect from the utility before connecting to backup power, which can cause brief outages. In contrast, closed *changeover* switches transfer seamlessly without interruption, maintaining switch reliability and ensuring continuous backup power.
- Open Transition: Brief power interruption, simpler design, lower cost, less switch reliability.
- Closed Transition: Seamless transfer, more complex, higher cost, *ideal* for critical loads.
- Switch Reliability: Closed transition offers higher reliability for sensitive equipment.
- Power Transfer: Closed transition minimizes disruption, better for maintaining continuous backup power.
Manual vs. Automatic Transfer Switches

Manual and automatic transfer switches serve different needs depending on your power management priorities. Manual switches require you to operate them physically, giving you control over switchgear operation but delaying response during outages. Automatic switches detect power loss and transfer loads seamlessly, ensuring continuous operation with minimal intervention. They excel in load prioritization, automatically switching to backup sources when necessary. Consider this comparison:
| Feature | Manual Transfer Switch | Automatic Transfer Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Response Time | Manual activation | Instantaneous |
| Switchgear Operation | User-controlled | Automated |
| Load Prioritization | Manual setup | Dynamic, automatic |
| Suitability | Emergency use | Critical systems |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Choosing depends on your need for quick response versus control and budget constraints. Additionally, reliable operation is essential for critical systems where automatic switching can prevent downtime and damage.
Essential Features to Consider When Choosing a Switch

When selecting an automatic or manual transfer switch, understanding key features guarantees you choose the right device for your needs. Focus on aspects like compatibility with your power supply, making sure it can handle your system’s voltage and current demands. Safety features are vital—look for protective mechanisms such as overload protection, fault detection, and grounding. Reliability is essential, so opt for switches with durable components and clear indicators. Ease of maintenance and installation also matter; choose a switch that’s straightforward to set up and service. Additional features like remote monitoring can enhance convenience. Remember, the right switch not only ensures seamless power transfer but also safeguards your equipment and personnel. Prioritize features that match your specific power setup and safety requirements. Proper selection can also help prevent cross-contamination risks associated with electrical faults or improper handling.
Common Applications for Different ATS Types

Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS) are widely used across various settings to guarantee reliable power transfer between sources. For emergency backup systems, you’ll find these switches essential, ensuring that backup generators automatically take over when the main power fails, minimizing downtime and protecting critical equipment. In data centers, ATS devices are vital for maintaining continuous operation, preventing data loss, and safeguarding sensitive information during power interruptions. Different ATS types suit specific applications; for example, open-transition switches are common in less critical environments, while closed-transition models are preferred for sensitive loads like data centers. Understanding these applications helps you choose the right ATS, ensuring seamless power transfer and enhancing your facility’s reliability and safety. Additionally, selecting the appropriate transfer switch type based on application needs can improve overall system efficiency and safety.
Installing and Maintaining Your Transfer Switch

Proper installation and regular maintenance of your transfer switch are key to ensuring reliable power transfer and safety. When installing, follow manufacturer instructions carefully, ensuring secure connections and proper grounding. Regular checks help identify wear, corrosion, or loose wiring. Incorporate surge protection to guard against power spikes, and consider a battery backup to maintain operation during outages. Routine maintenance includes cleaning contacts, testing the system, and verifying alarm functions. Always turn off power before servicing to prevent accidents. Periodic inspections help extend your transfer switch’s lifespan and ensure it operates correctly when needed. Keep detailed records of maintenance activities. Proper care guarantees your system remains dependable, protecting your home and equipment from power disturbances. Additionally, understanding Gold IRA options can be a smart way to diversify your investment portfolio for long-term financial security.
How to Choose the Right ATS for Your Needs

Are you unsure which transfer switch suits your home’s power needs? To improve your power outage preparedness, you need an ATS compatible with your generator. Start by evaluating your power requirements—larger homes with multiple appliances need a higher capacity switch. Check your generator’s wattage and ensure the ATS supports it for seamless generator compatibility. Consider whether you want a manual or automatic switch, based on how quickly you need backup power to activate. Think about future expansion—will you add appliances later? Also, appraise the switch’s reliability and ease of use. Selecting the right ATS involves matching it to your generator and ensuring it provides dependable, automatic transfer during outages. Proper choice guarantees safety, convenience, and uninterrupted power when you need it most.
Additionally, understanding best vacuums for dust removal in 2024 can help ensure your home environment stays healthy during power outages by maintaining clean air quality.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does an Automatic Transfer Switch Impact Overall Power System Reliability?
An automatic transfer switch boosts your power system’s reliability by providing seamless backup power during outages, ensuring critical systems stay operational. It quickly switches to backup power sources, minimizing downtime and maintaining system resilience. This automatic action reduces human error and delays, keeping your operations smooth and secure. Overall, it’s a essential component that enhances your system’s dependability and resilience against power interruptions.
Can Automatic Transfer Switches Be Integrated With Renewable Energy Sources?
Yes, automatic transfer switches can be integrated with renewable energy sources, enabling seamless renewable integration. They work well in hybrid systems, switching between traditional generators and renewable power like solar or wind. This setup guarantees continuous power supply, enhances system reliability, and optimizes renewable energy use. Properly configured, an ATS helps manage multiple energy sources efficiently, supporting sustainable and resilient power solutions for your needs.
What Are the Common Troubleshooting Issues With Different ATS Types?
Troubleshooting transfer switches can be tricky, but you can tackle common issues with confidence. Faulty wiring often causes inconsistent switching, while improper grounding sparks surges and system failures. You might notice delays or failures to transfer power correctly. Regularly inspect connections, tighten loose wires, and verify grounding practices. By pinpointing these problems early, you prevent potential power outages and ensure your automatic transfer switch operates smoothly and safely.
Are There Specific Safety Standards for Automatic Transfer Switches?
Yes, there are specific safety standards for automatic transfer switches. You need to follow safety regulations set by organizations like UL and IEC, which make certain your ATS operates safely under various conditions. Certification standards verify that the switch meets critical safety and performance criteria. Always choose ATS devices that are properly certified, and adhere to local electrical codes to prevent hazards and ensure reliable operation.
How Do Environmental Factors Affect the Performance of Transfer Switches?
Environmental factors critically impact your transfer switch’s performance through environmental durability and installation considerations. Harsh conditions like moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures can cause corrosion, electrical faults, or failure. To guarantee ideal operation, you should select a switch rated for your environment, install it in a protected location, and maintain it regularly. Proper planning for environmental durability and installation considerations helps your transfer switch operate reliably, even in challenging conditions.
Conclusion
Choosing the right automatic transfer switch is like finding the perfect tool for a job—you want reliability, ease of use, and the right features. By understanding the different types and applications, you can confidently select an ATS that keeps your power steady, just like a steady hand guides a ship through calm or stormy seas. With proper installation and maintenance, your switch will serve you well, ensuring your power stays on when you need it most.









