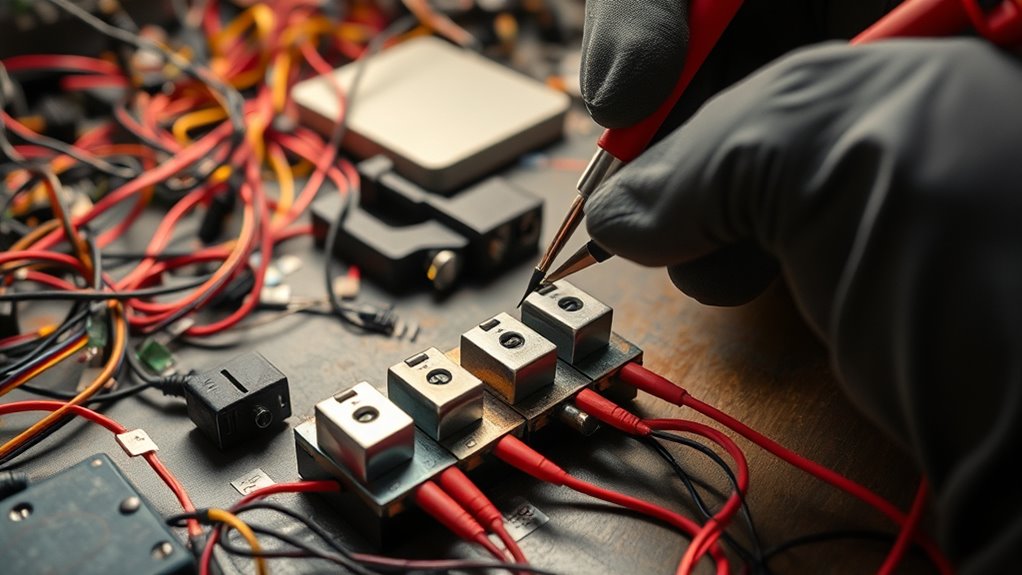
When troubleshooting a faulty voltage regulator, start by visually inspecting for swollen or leaking capacitors, which often cause instability. Check for excessive heat and make sure cooling components like fins and fans are clean and functioning properly. Use a multimeter to measure the output voltage against specifications and look for loose wiring or damaged resistors. If internal parts are damaged, replacing capacitors or the entire unit might be necessary. More tips can help you fix the issue effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Perform visual inspection for damaged, leaking, or bulging capacitors around the regulator.
- Use a multimeter to measure output voltage and compare it to specifications.
- Check for loose connections, damaged wiring, or faulty resistors affecting regulator performance.
- Ensure proper heat dissipation by cleaning fins, replacing thermal pads, and adding cooling fans if needed.
- Replace malfunctioning capacitors and consider replacing the entire regulator if internal damage is evident.
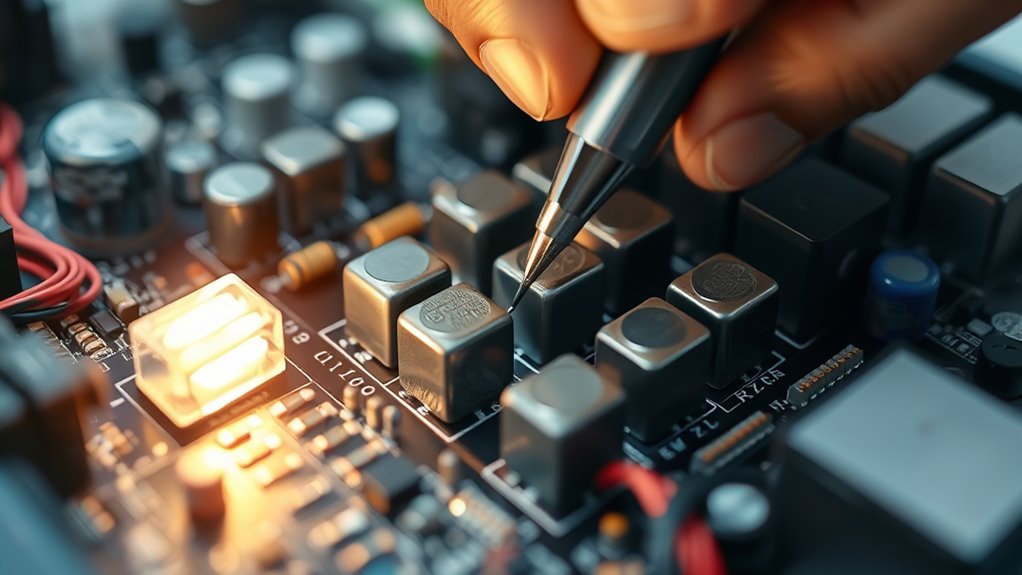
Have you ever experienced unstable power supply or equipment malfunctions? If so, faulty voltage regulators might be the culprit. These devices guarantee your electrical systems run smoothly by maintaining consistent voltage levels. When they malfunction, your equipment can face erratic power, leading to potential damage or operational issues. One common cause of such problems is issues within the regulator’s internal components, like capacitors. Over time, capacitors can degrade, causing fluctuations in voltage output. When troubleshooting, think about performing capacitor replacement if you notice swelling, leakage, or bulging. Replacing faulty capacitors can restore stability, but it’s equally important to address heat dissipation. Excess heat can accelerate capacitor failure and other internal component issues. Ensuring proper heat dissipation might involve cleaning cooling fins, replacing thermal pads, or adding cooling fans to prevent overheating. Efficient heat management helps extend the lifespan of your voltage regulator and prevents future failures.
When you suspect a capacitor problem, start by inspecting the regulator visually. Look for signs of damage or leakage around the capacitors. If you find any, carefully remove the faulty component and replace it with a new one of the same specifications. Remember, capacitors store electrical energy, so always discharge them safely before handling. After replacement, test the regulator to see if the voltage output stabilizes. If instability persists, check whether heat dissipation is adequate. Over time, dust buildup can block airflow, trapping heat inside the regulator. Regular cleaning of vents, fins, and fans helps maintain ideal cooling. If your regulator is enclosed in a tight space, think about installing additional cooling solutions to prevent overheating. Also, understanding the Kia Tuning options can provide insights into how electrical stability impacts performance modifications.
Another key step is to verify that all other components are functioning correctly. Loose connections, damaged wiring, or faulty resistors can also cause voltage irregularities. Use a multimeter to measure the output voltage and compare it with the regulator’s specifications. If you notice persistent issues despite capacitor replacement and heat dissipation improvements, it might be time to think about replacing the entire regulator. Sometimes internal component damage is too extensive for simple repairs, especially in older units. Proper troubleshooting involves systematically checking each part, making sure that heat dissipation is enhanced, and replacing capacitors when necessary. By addressing these factors, you can restore your voltage regulator’s performance and protect your equipment from voltage-related damage. Remember, regular inspection and maintenance are key to preventing future failures and guaranteeing your electrical systems stay reliable.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Prevent Voltage Regulator Failure in the First Place?
To prevent voltage regulator failure, you should perform regular preventative maintenance, including checking connections and testing performance. Guarantee proper installation by following manufacturer guidelines carefully, avoiding overloading the regulator, and using suitable components. Keep the environment clean and cool, as heat and dust can cause damage. Regular inspections help you catch issues early, prolonging the regulator’s lifespan and maintaining stable voltage output.
Can a Faulty Voltage Regulator Cause Damage to Other Components?
A faulty voltage regulator is like a loose cannon, and yes, it can damage other components. When it malfunctions, it causes voltage fluctuations that impact the lifespan of your parts, potentially frying sensitive electronics. Over time, the damage worsens, leading to costly repairs. To protect your equipment, monitor voltage levels regularly and replace a faulty regulator promptly, ensuring stable power flow and safeguarding your system’s health.
What Are the Signs of Intermittent Voltage Regulator Issues?
You might notice warning signs like flickering lights, unexpected system resets, or irregular voltage readings. To troubleshoot, start by checking the voltage output with a multimeter, ensuring it stays within specs. Look for loose connections or damaged components. If the voltage fluctuates unexpectedly, replace or repair the regulator. Regularly testing the system helps catch issues early and prevents further damage caused by intermittent voltage regulation problems.
How Often Should Voltage Regulators Be Tested or Replaced?
You should test your voltage regulator according to your vehicle’s maintenance schedule, typically every 30,000 to 50,000 miles. Replace it if you notice signs of failure, such as dimming lights or battery issues. Regular testing frequency helps catch problems early, preventing breakdowns. If your vehicle experiences electrical problems or irregular voltage fluctuations, it’s wise to check the regulator sooner rather than later to guarantee peak performance.
Are There Specific Tools Recommended for Diagnosing Regulator Problems?
Imagine holding a multimeter in your hand, its probes ready to reveal hidden faults. For diagnosing regulator problems, you’ll want diagnostic tools like a digital multimeter, oscilloscope, and test light. These testing procedures help you measure voltage levels and observe fluctuations precisely. By using these tools, you can pinpoint issues quickly and accurately, ensuring your regulator functions properly before it causes more significant electrical problems.
Conclusion
Now that you know how to troubleshoot faulty voltage regulators, you can save time and avoid unnecessary replacements. Remember, a faulty regulator can cause equipment damage or failure, so catching issues early is key. Did you know that approximately 30% of electronic device failures are due to power regulation problems? Staying vigilant and understanding common signs can keep your devices running smoothly, saving you both money and frustration in the long run.