Understanding automatic transfer switch types and their safety features is essential for reliable backup power. Whether you choose manual, automatic, or bypass switches, each has safety considerations like grounding, interlocks, and maintenance needs. Open and closed transfer systems also impact safety during power changes. Proper installation, load management, and emergency shutoff features help prevent hazards like shocks or fires. If you want to guarantee your system remains safe, continue exploring the key safety tips and best practices.
Key Takeaways
- Safety features like grounding, interlocks, and clear indicators prevent electrical shocks and backfeeding hazards.
- Selecting the appropriate transfer type (open or closed) impacts safety and reliability during power transfer.
- Proper installation, adherence to codes, and correct wiring are essential to prevent faults and electrical fires.
- Regular maintenance and testing ensure the ATS operates safely and detects issues early.
- Operator training and emergency protocols are vital for safe handling and response during power failures.
The Basics of Automatic Transfer Switches and Their Functions

Automatic transfer switches (ATS) are essential devices that guarantee your power supply remains uninterrupted during outages. They automatically detect power failures and switch from your main power source to a backup generator, ensuring continuous operation. When selecting an ATS, generator compatibility is key; it must match your generator’s voltage and capacity to work seamlessly. Environmental considerations also matter, as the switch should tolerate your installation environment—whether indoors or outdoors—and resist moisture, dust, or extreme temperatures. An ATS simplifies your backup power system, reducing manual intervention and preventing power interruptions. By understanding these core functions, you affirm a reliable, safe connection between your power sources and loads, keeping your operations running smoothly regardless of external conditions. High reliability in ATS design is crucial to ensure consistent performance in critical situations.
Types of Automatic Transfer Switches: Manual, Automatic, and Bypass

When choosing an automatic transfer switch, it’s important to understand the different types available—manual, automatic, and bypass. Manual switches require you to operate them manually during power changes, offering simplicity but less convenience. Automatic switches detect power loss and switch seamlessly, providing generator compatibility and continuous operation. Bypass switches let you isolate the transfer switch for maintenance, ensuring safety and environmental considerations. Consider your setup’s needs and environment when selecting. For example, an automatic switch suits critical loads, while manual might suffice for less essential equipment. Bypass options are valuable for ongoing maintenance without interrupting power. Additionally, understanding the AI vulnerabilities associated with some switch controls can help in selecting more secure systems.
Key Safety Features in Different ATS Designs

Choosing the right ATS involves more than just matching it to your power needs; safety features play a critical role in protecting both equipment and personnel. Grounding safety is essential in preventing electrical shocks and equipment damage, so look for designs with robust grounding systems. Many ATS models include safety interlocks that prevent simultaneous connection to both sources, reducing the risk of backfeeding. Operator training is essential to guarantee safe operation; well-designed systems provide clear indicators and fail-safes to guide users through proper procedures. Regular maintenance and familiarization with safety features help prevent accidents. Additionally, understanding Grounding safety measures ensures comprehensive protection against electrical hazards. By selecting an ATS with thorough grounding safety measures and ensuring your team is trained, you notably reduce risks and enhance overall system safety.
Transfer Mechanisms: Open vs. Closed Transition Systems

When choosing between open and closed transition systems, you’ll notice differences in how the transfer process occurs. Mechanical switches disconnect and connect circuits directly, while electrical switching offers smoother, seamless transfers. Safety and reliability are key factors to contemplate, as each system impacts risk levels and operational stability differently. Additionally, considering energy-efficient models can contribute to safer and more reliable operation by reducing the risk of overheating or electrical failures.
Transition Process Differences
Understanding the differences in changeover processes between open and closed transfer switch systems is essential for selecting the right solution for your power needs. In an open transition system, the transition process involves a brief outage as the switch disconnects from the failed source before connecting to the backup power. The switching sequence is sequential, creating a moment where both sources are disconnected. Conversely, a closed transition system maintains continuous power by overlapping the sources during the transition, ensuring minimal or no outage. The switching sequence in a closed system involves a seamless transfer, with the switch momentarily paralleling both sources. Recognizing these differences helps you choose a transfer switch that aligns with your reliability requirements and operational priorities. Utilize vertical storage solutions to better understand how organized systems can support efficient power management and safety during transfer processes.
Mechanical vs. Electrical Switching
Mechanical and electrical switching mechanisms determine how transfer switches operate during a transfer process. Mechanical systems rely on physical contact, offering high mechanical durability but requiring regular maintenance. Electrical switching uses solenoids or motorized contacts, providing faster transfer times and easier automation. Open transition systems disconnect the load before connecting the new power source, minimizing electrical grounding issues but causing brief outages. Closed transition systems briefly connect both sources, ensuring seamless power transfer but increasing complexity and potential wear. Here’s a comparison:
| Feature | Mechanical Switches | Electrical Switches | Transition Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durability | High Mechanical Durability | Less Mechanical Wear | Open or Closed |
| Grounding Control | Manual grounding needed | Can automate grounding | Open or Closed |
| Transfer Speed | Slower | Faster | Open or Closed |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required | Less frequent maintenance | N/A |
| Reliability | Very reliable, proven design | Depends on electronics | Open or Closed |
Additionally, advancements in transfer switch technology continue to enhance reliability and safety features.
Safety and Reliability Factors
Choosing between open and closed changeover systems markedly impacts safety and reliability. Open transfer mechanisms switch sources gradually, reducing risk during power transitions, but may expose equipment to environmental factors like dust or moisture. Closed systems, on the other hand, instantly switch sources, minimizing outages and surge risks, but require more precise control to prevent backfeeding or damage. Surge protection is critical in both systems to guard against voltage spikes that can harm sensitive components. Environmental considerations, such as temperature fluctuations or humidity, influence the durability of the transfer system. A closed transition system generally offers improved reliability by ensuring seamless power transfer, but it demands rigorous maintenance and safeguards. Your choice should reflect your operational environment, safety priorities, and the need for reliable power continuity. Additionally, understanding the Types of Transfer Mechanisms is essential for selecting the appropriate system for your specific safety and reliability requirements.
Understanding Load Management and Safety Implications
Proper load management is vital to guarantee that your automatic transfer switch (ATS) operates safely and reliably during power outages. By implementing load prioritization, you ensure essential systems receive power first, preventing overloads that could damage equipment or cause failures. Safety protocols must be followed to avoid risks like electrical faults or fires, especially when managing multiple loads. Regularly assess your load capacity to prevent exceeding the switch’s limits, which could compromise safety. Using load management techniques helps maintain system stability and reduces the chance of outages or damage. Remember, balancing loads effectively is key to safe operation, protecting both your equipment and personnel. Prioritize critical loads and adhere to safety protocols to ensure your ATS functions at its best during emergencies. Additionally, understanding load capacity is crucial to ensure your system remains within safe operational limits.
Proper Installation Practices to Ensure Safety

To guarantee safety when installing an automatic transfer switch (ATS), you must follow established electrical codes and manufacturer instructions carefully. Proper installation involves adhering to wiring standards and correct grounding procedures to prevent electrical hazards. Ensure all wiring is neat, secure, and labeled clearly. Use the correct gauge wire for your system and verify connections are tight. Ground the ATS properly to prevent electrical shock and equipment damage. Keep the installation area dry and free of clutter. Confirm that your grounding procedures comply with local regulations to enhance safety and system reliability. Visualize the process as you: – Carefully routing wires along designated paths – Connecting grounding cables securely to grounding rods – Double-checking all wiring for compliance with standards – Installing protective covers over terminals – Testing the system before powering up Proper installation practices are critical for ensuring safety and system longevity.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection for Safe Operation
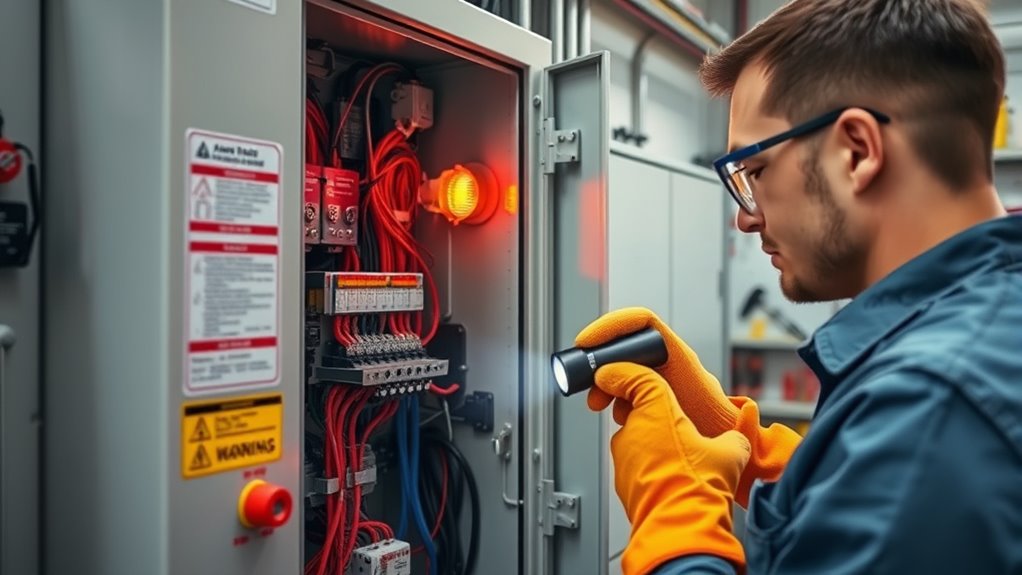

Regular maintenance and inspections are essential to keep your automatic transfer switch operating safely and reliably. You should follow routine inspection procedures, checking for signs of wear, corrosion, or loose connections. Implementing preventive maintenance strategies helps identify issues early and extend the switch’s lifespan. Additionally, understanding the city dynamics can help in planning maintenance schedules that minimize disruptions during power outages.
Routine Inspection Procedures
Routine inspection procedures are essential to guarantee the safe and reliable operation of automatic transfer switches. Regular checks help identify issues before they cause failures, ensuring smooth power flow during outages. You should verify the battery backup’s condition, ensuring it’s charged and free of corrosion. Inspect connections for tightness and signs of wear. Test the switch’s operation by simulating power loss to confirm it transfers seamlessly. Check for any abnormal noises or overheating. Review control panel indicators for error alerts. Examine the transfer mechanism for dirt or debris that could hinder movement. Confirm that all safety features are functional. Keep the environment clean and dry. These steps help maintain ideal performance and prevent unexpected downtime.
Preventive Maintenance Strategies
Implementing effective preventive maintenance strategies is essential to guarantee the safe and reliable operation of automatic transfer switches. Regularly inspecting the battery backup ensures the system can function during power outages, preventing unexpected failures. Check battery connections for corrosion, and replace batteries before they fail. Additionally, inspecting for potential power surges helps protect the switch from electrical damage; installing surge protectors can mitigate this risk. Keep the transfer switch clean and free of dust, which can cause overheating or malfunction. Test the switch periodically to verify proper operation during power transfer. By proactively addressing issues related to battery backup and power surges, you reduce downtime and ensure safety, keeping your system resilient and ready for any emergency.
Common Hazards Associated With ATS and How to Mitigate Them

While automatic transfer switches (ATS) are essential for ensuring reliable power transfer, they also pose certain hazards if not properly maintained or operated. Hazardous voltages can occur during switching, risking electrical shock. Improper grounding increases the danger of electrical faults and equipment damage. You should be aware of these risks to prevent accidents and equipment failure.
Key hazards include:
- Exposure to hazardous voltages during maintenance or faults
- Electric shocks from ungrounded or poorly grounded systems
- Arc flash incidents caused by faulty contacts
- Damage from improper wiring or connections
- Fire risks due to overheating or electrical faults
To mitigate these risks, ensure regular inspections, proper grounding, and adherence to safety protocols at all times.
Emergency Shutoff Features and Their Importance
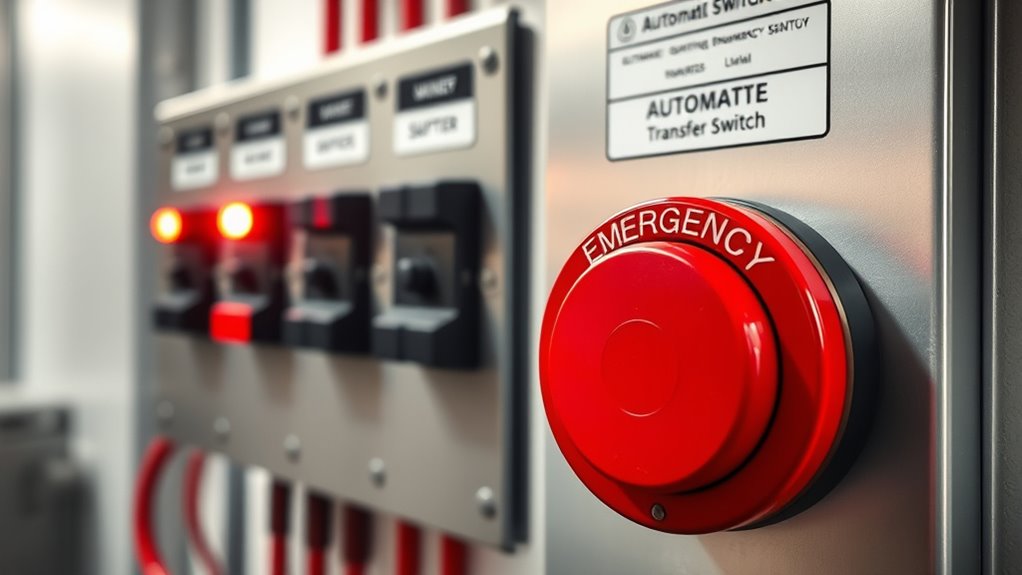

Have you ever considered what could happen if an emergency arises during power transfer? Emergency shutoff features are essential for your safety. They allow you to quickly disconnect power and prevent damage or injury. Many systems include a battery backup that guarantees the emergency shutoff remains operational even if main power fails. A user interface makes activating these shutoffs straightforward, giving you clear options in urgent situations. Without a reliable emergency shutoff, risks increase, including electrical fires and equipment damage. Ensuring your ATS has these features, along with an intuitive interface, enhances safety and control during critical moments. Remember, quick action can prevent disasters—so prioritize emergency shutoff capabilities when choosing or maintaining your automatic transfer switch.
Best Practices for Selecting and Using ATS Safely

Choosing the right automatic transfer switch (ATS) is crucial for ensuring safe and reliable power transfer. To do this, consider your system’s needs and environmental factors. Always select an ATS compatible with your battery backup system to ensure smooth startup during outages. Protect against power surges by installing appropriate surge suppressors. Regularly inspect and maintain the switch to prevent faults. Use proper wiring techniques to avoid accidental shorts or shocks. Be aware of your load capacity to prevent overloads. When installing, ensure safety protocols are followed to avoid electrical hazards.
- Visualize a switch seamlessly transferring power from utility to backup, keeping equipment safe.
- Imagine a surge protector shielding your system during voltage spikes.
- Picture a technician inspecting connections for secure wiring.
- Think of a battery backup ready to power your facility during outages.
- Envision a clear, labeled panel for easy operation and troubleshooting.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does an ATS Prevent Electrical Fires During Transfer?
An ATS prevents electrical fires during shift by ensuring safe generator operation through circuit protection and generator safety features. It automatically disconnects the load from the utility and connects it to the generator, preventing overloads and short circuits that can cause fires. The switch’s built-in safety mechanisms, like circuit breakers, monitor electrical flow, detect faults, and shut down the system if needed, maintaining safe operation during power transitions.
What Are the Safety Differences Between Manual and Automatic ATS?
Did you know that manual transfer switches account for nearly 60% of electrical safety incidents? When comparing safety, manual ATS relies on user action, which increases manual safety concerns like improper operation. Automatic ATS reduces hazards by switching power seamlessly and automatically, minimizing human error. However, automatic systems can pose risks like potential electrical faults. Always guarantee proper installation and maintenance to stay safe, regardless of switch type.
Can Improper Load Management Cause Safety Issues With ATS?
Improper load management can definitely cause safety issues with your ATS. If you don’t balance loads properly, it can lead to overloads, increasing the risk of faults or electrical fires. Fault detection systems can catch these problems early, but if ignored, they might not prevent damage. Regularly balancing your loads and ensuring fault detection is active helps maintain safety, preventing potential hazards and protecting your equipment and personnel.
Are There Specific Safety Standards for ATS Installation Worldwide?
Like a trusty knight’s armor, safety standards protect you during ATS installation. Yes, there are specific safety standards worldwide, such as UL and IEC, ensuring standards compliance and safe installation guidelines. These standards cover electrical connections, grounding, and testing procedures, helping prevent hazards. Always follow these guidelines diligently, much like following a blueprint for a time machine, to guarantee safety and proper operation of your automatic transfer switch system.
What Training Is Recommended for Safe ATS Operation?
You should complete certified training programs that focus on ATS operation to guarantee safety. Look for courses covering installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting, as these meet industry standards and training requirements. Certification programs, like those offered by recognized electrical safety authorities, validate your skills and knowledge. Regularly updating your training keeps you current with safety protocols and best practices, helping you operate automatic transfer switches safely and effectively.
Conclusion
By understanding the different types and safety features of automatic transfer switches, you hold the key to a resilient electrical fortress. Regular maintenance and mindful operation act as your shield against unforeseen hazards, ensuring your power system remains steadfast. Think of your ATS as the silent guardian, seamlessly switching your lifelines in times of crisis. With knowledge and vigilance, you turn potential chaos into a well-orchestrated symphony of safety and reliability.









