To properly ground and bond your standby system, you need to understand the purpose of grounding, choose the right grounding electrode system, and guarantee a continuous, low-resistance path for fault currents. You should bond all system components securely, use the correct conductors and connectors, and keep everything compliant with electrical codes. Regular inspections and maintenance are key to safety and reliability. Stay with us, and you’ll discover everything you need to ensure your system’s safety and efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Proper grounding directs fault currents safely to earth, preventing equipment damage and ensuring safety during surges.
- Bonding all metal parts maintains uniform voltage, reducing shock risks and preventing dangerous potential differences.
- Use approved grounding electrodes and connectors, and verify compliance with local electrical codes for safety and reliability.
- Regular inspection and testing of grounding and bonding systems help identify corrosion, loose connections, or system failures early.
- Proper design and maintenance of grounding paths ensure system stability, safety, and adherence to electrical standards.
Understanding the Importance of Proper Grounding and Bonding
Have you ever wondered why proper grounding and bonding are so critical in electrical systems? They play an essential role in ensuring safety and system reliability. Proper grounding provides a path for excess electrical energy, such as a lightning strike or power surge, directing it safely into the ground. Lightning grounding is essential to protect your equipment from destructive sparks and voltage spikes. Bonding, on the other hand, ensures all metal parts are connected, preventing dangerous voltage differences. Together, grounding and bonding help with surge protection by minimizing the risk of electrical shock and damage. Proper grounding techniques are vital for maintaining system stability and compliance. Without them, your system becomes vulnerable to unpredictable electrical events, increasing safety hazards and potential equipment failures. Prioritizing proper grounding and bonding keeps your electrical system safe, stable, and compliant.
Differentiating Between Grounding and Bonding

You need to understand the difference between grounding and bonding because they serve distinct purposes. Grounding provides a safe path for electrical faults to reach the earth, while bonding connects conductive parts to guarantee they stay at the same electrical potential. Recognizing their functions helps you install and maintain electrical systems safely and correctly. Additionally, understanding electrical safety practices is essential for responsible system management.
Grounding vs. Bonding
While grounding and bonding are often mentioned together in electrical systems, they serve distinct purposes. Grounding provides a safe path for fault currents, helping with surge protection and lightning grounding by directing excess energy safely into the earth. Bonding, on the other hand, connects metal parts to ensure they are at the same electrical potential, preventing dangerous voltage differences. This prevents electrical shock hazards and equipment damage. Grounding establishes a reference point for the system, while bonding ensures all conductive parts are interconnected. Both are essential for safety, but they operate differently. Proper grounding reduces the risk of electrical fires and protects equipment during surges, whereas bonding maintains system integrity by preventing potential differences that could cause shocks or damage during fault conditions. Understanding electrical safety is crucial for designing and maintaining effective grounding and bonding systems.
Purpose and Function
Understanding the purpose and function of grounding and bonding is essential because, although they work together to enhance electrical safety, each serves a distinct role. Grounding provides a safe path for fault currents to reach the earth, reducing shock hazards and protecting equipment. Bonding techniques, on the other hand, ensure all conductive parts are connected to maintain a common potential, preventing dangerous voltage differences. Avoid grounding myths that suggest grounding alone prevents all shocks—it’s just one part of a thorough safety system. Bonding techniques complement grounding by securing equipment to reduce arcing and improve fault detection. Recognizing these differences helps you implement proper grounding and bonding practices, ensuring your standby system remains safe, reliable, and compliant with electrical codes. Additionally, understanding the basics of soaring and gliding can help illustrate how controlled systems maintain stability and safety through proper connection and grounding practices.
Identifying the Correct Grounding Electrode System
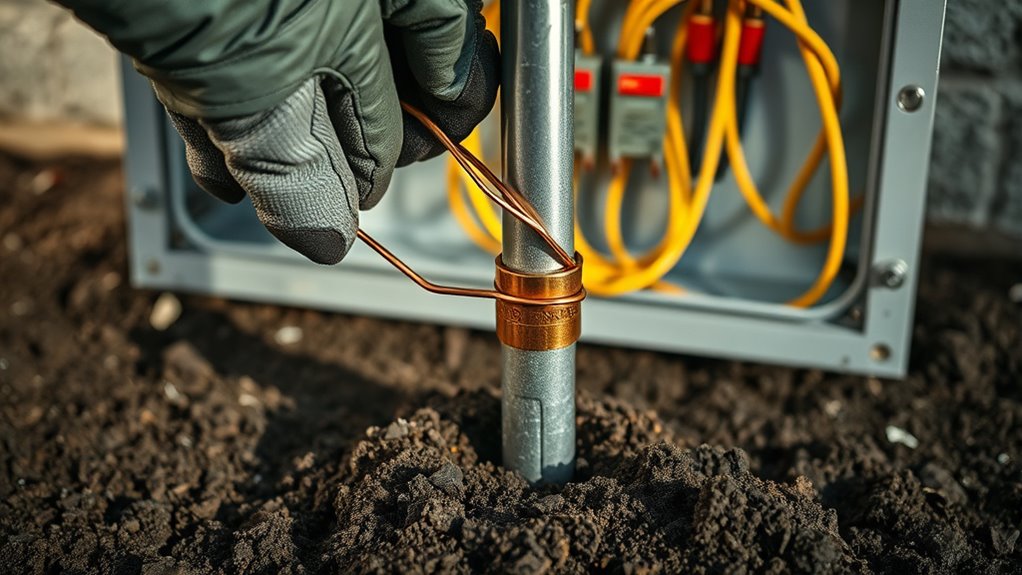

How do you determine the correct grounding electrode system for your installation? First, identify the grounding electrode types available in your area, such as concrete-encased electrodes, ground rods, or metal water pipes. Next, consider the electrode installation methods suitable for your site—whether driving rods, attaching to existing structures, or embedding in concrete. Your choice depends on local codes and the structure’s environment. Use this table to guide your selection:
| Electrode Type | Installation Method | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|
| Concrete-encased electrode | Embed in concrete foundation | New construction |
| Ground rod | Drive into soil | Remote or new sites |
| Metal water pipe | Attach to existing pipe | Buildings with metal plumbing |
| Structural steel | Connect to structural elements | Large commercial facilities |
| Building steel | Bond to steel framework | Industrial setups |
Always verify with local codes before proceeding. Additionally, it’s important to understand the grounding system requirements to ensure safety and compliance.
Establishing a Continuous Equipment Grounding Path
Establishing a continuous equipment grounding path is essential for safety and proper system operation. Without it, faults may not trip the breaker, risking shock hazards. To guarantee continuity:
A continuous grounding path ensures safety and reliable system operation.
- Use a proper grounding wire that connects all metallic parts of the system securely.
- Install bonding straps where connections might loosen or corrode over time.
- Avoid splicing grounding wires with unapproved connectors; keep the path intact.
- Check that all system components, including transfer switches and enclosures, are properly bonded.
- Regular inspections and testing of grounding connections can help ensure ongoing safety and compliance with grounding standards.
Properly Bonding Transfer Switches and System Components
Properly bonding transfer switches and system components guarantees a safe and reliable electrical system. To do this, you must assure a solid connection within your grounding system using effective bonding techniques. This involves connecting the transfer switch enclosure, equipment grounding conductors, and system components to create a continuous, low-impedance path for fault currents. Proper bonding prevents potential differences that could cause shocks or equipment damage. Always verify that all connections are tight and free of corrosion. Use appropriate grounding and bonding materials as specified by electrical codes. Remember, the goal is to establish a secure, conductive bond that maintains system stability and safety during normal operation and fault conditions. Proper bonding techniques are essential for the overall integrity of your standby power system. Additionally, understanding AI Security concerns can help inform the development of safer, more resilient electrical systems in the future.
Managing Grounding for Multiple Power Sources

Managing grounding for multiple power sources requires careful coordination to guarantee system safety and reliability. Misunderstanding bonding techniques can lead to grounding misconceptions that compromise proper operation. To avoid these issues, consider the following:
- Ensure a common grounding point for all sources to prevent potential differences.
- Use proper bonding techniques to connect neutral and grounding conductors correctly.
- Verify that each power source’s grounding system is compatible with the standby system.
- Regularly inspect and test grounding connections to maintain system integrity.
- Incorporate active listening into your approach to promptly identify and address grounding issues before they escalate.
Using the Right Conductors and Connectors for Bonding

Choosing the correct conductors and connectors is essential for effective bonding. You need materials that are dependable, secure, and meet all local code requirements. Making the right selections ensures safety and compliance in your electrical system. Incorporating proper grounding methods can also enhance overall system safety and performance.
Selecting Appropriate Materials
Selecting the right conductors and connectors is essential to guarantee effective grounding and bonding systems. Proper material selection ensures compatibility between conductors and connectors, preventing corrosion and ensuring durability. You must choose materials that match the system’s electrical requirements and environmental conditions. Using incompatible materials can lead to poor conductivity and potential failure. Focus on conductor compatibility to avoid issues over time. Here are key points to consider:
- Match conductor material with connector material to prevent galvanic corrosion
- Use conductors rated for the system’s current and voltage
- Opt for corrosion-resistant materials in harsh environments
- Verify that connectors meet industry standards for grounding and bonding
- Incorporate AI-driven tools to assist in selecting materials that optimize system performance and longevity
Ensuring Secure Connections
To guarantee secure connections in grounding and bonding systems, you must use the right conductors and connectors designed for the specific application. Choose a grounding conductor that meets the required gauge and material specifications, making sure it can handle the system’s fault current safely. Proper connectors, such as lugs and clamps, must be rated for the conductor type and environment to maintain a solid, corrosion-resistant connection. When bonding, use a bonding jumper to connect metal parts and create an effective grounding path. Ensure all connections are tight and free of corrosion or debris to prevent resistance and potential failures. Using appropriate conductors and connectors helps maintain system integrity, reduces electrical hazards, and ensures reliable operation of your standby system.
Complying With Codes
Ensuring your bonding and grounding systems comply with applicable codes is essential for safety and reliability. Using the right conductors and connectors helps prevent grounding myths and bonding misconceptions that could compromise your system. Always verify that your materials meet local electrical standards, avoiding shortcuts that might seem convenient but are unsafe. Proper conductors reduce resistance and ensure a solid connection, minimizing electrical hazards. Connectors must be rated for your system’s voltage and current, preventing failures. Remember, code compliance isn’t just about legality; it’s about protecting lives and property.
- Use only approved grounding conductors and connectors
- Confirm compatibility with local electrical codes
- Avoid grounding myths that suggest cheaper materials are sufficient
- Regularly inspect for signs of bonding misconceptions or deterioration
Ensuring Compliance With National and Local Electrical Codes

Compliance with national and local electrical codes is essential to guarantee safety and proper functioning of electrical systems. To meet these standards, you must follow grounding best practices and bonding techniques outlined in your area’s regulations. Use proper grounding electrodes, secure connections, and appropriate conductor sizes. Ensuring code compliance minimizes risks and legal issues while maintaining system integrity. Here’s a quick overview:
| Code Requirement | Description | Example Application |
|---|---|---|
| Grounding Conductors | Use approved materials and sizes | Copper wire, #8 gauge |
| Bonding Techniques | Connect all metallic parts properly | Bonding jumper to panel |
| Grounding Electrode System | Install proper grounding rods | Copper rod driven into soil |
| Inspection & Certification | Obtain approvals before use | Local electrical inspector |
Always verify local amendments, and keep documentation to prove compliance.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance of Grounding and Bonding Systems

Regular inspection and maintenance of grounding and bonding systems are essential to guarantee ongoing safety and reliable electrical performance. Regular checks help identify issues like corrosion, which can compromise system integrity. Environmental considerations, such as moisture or chemical exposure, require you to adapt maintenance routines accordingly. To keep your system in top shape:
Regularly inspect and maintain grounding systems to ensure safety and reliability.
- Inspect for corrosion and address it promptly
- Ensure connections are tight and free of corrosion
- Test grounding resistance regularly
- Consider environmental factors that may affect system longevity
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Environmental Conditions Affect Grounding and Bonding Effectiveness?
Environmental conditions markedly impact grounding and bonding effectiveness. Soil conductivity varies with moisture levels; wetter soil typically offers better conductivity, reducing resistance, while dry soil increases resistance, weakening the system. High moisture levels improve grounding, ensuring safety and system reliability. Conversely, dry or frozen conditions lower conductivity, making grounding less effective. You should regularly assess soil moisture and adjust grounding systems accordingly to maintain ideal safety and performance.
What Are Common Mistakes to Avoid During Grounding System Installation?
Avoid common grounding errors like improper conductor sizing or insecure connections, which can compromise system safety. Don’t overlook bonding oversights, such as failing to adequately bond metallic parts, leading to potential shock hazards. Always follow manufacturer instructions, double-check connections, and guarantee grounding paths are continuous and properly terminated. Stepping back to verify the installation can prevent costly mistakes and enhance system reliability and safety during operation.
How Does Grounding Differ for Portable Versus Permanent Standby Systems?
You should understand that portable grounding requires flexible bonding techniques to adapt to different setups, unlike permanent systems that use fixed grounding electrodes. For portable systems, guarantee you have reliable grounding cords and attach them securely to grounded objects, while bonding techniques must prevent potential differences. Permanent systems, on the other hand, rely on fixed grounding rods and consistent bonding methods to maintain a continuous ground path. Properly distinguishing these ensures safety and code compliance.
What Are the Safety Protocols During Grounding System Testing?
During grounding system testing, you should follow strict grounding procedures to guarantee safety. Always wear appropriate safety gear, such as insulated gloves, helmets, and eye protection. Verify that testing equipment is properly grounded and de-energized before starting. Maintain clear communication with team members, and keep a safe distance from live parts. These precautions help prevent electric shock and ensure safe, effective testing of the grounding system.
How to Troubleshoot Grounding and Bonding Problems in Existing Systems?
To troubleshoot grounding and bonding problems, start by inspecting grounding materials for corrosion or damage. Check bonding connectors to guarantee they’re properly secured and free of corrosion. Use a multimeter to verify continuity between grounding points and the system. If readings are inconsistent, replace damaged grounding materials or bonding connectors. Regularly test the system to identify issues early and maintain a safe, reliable connection to prevent electrical faults.
Conclusion
By following these nine grounding and bonding rules, you build a reliable shield protecting your standby system like a fortress. Proper grounding isn’t just a technical requirement; it’s the heartbeat that keeps your system safe and ready when you need it most. Stay diligent with inspections and maintenance, and remember, a well-grounded system is your silent guardian—standing watch quietly, so you can rest easy knowing your power is always protected.









